NAD Supplementation And Cognitive Health - Prevention And Restoration
Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide (NAD), a powerful natural compound found in every cell of the human body, serves as a critical coenzyme which powers vital biochemical reactions and is essential for optimal cellular functioning and repair. Like so many other bodily compounds, NAD levels decline as you age and this decline contributes to many of the often worrying changes you are likely to experience as you grow older, such as a decrease in cognitive functioning, a reduction in bone density and a decline in muscle strength.
As important as the conservation of bone density and muscle strength are to your well being as you grow older, it’s the preservation and possibly even the prospect of rejuvenation of cognitive functioning that is likely to occupy the primary position on your list of concerns. Supplementation to increase your level of NAD has a wide range of powerful anti-aging effects including the promotion of brain health.
But how does NAD work in your body to protect your brain and could optimal levels of this vital compound possibly even reverse some of the cognitive effects of aging?
The Neurovascular Unit or NVU
Recent research is making it increasingly clear that your brain cells and the health of those cells do not exist in isolation. When scientists speak of keeping the brain healthy, they are really referring to the relatively new concept of the NVU or neurovascular unit. The NVU is the interface between your brain cells (neurons) and the blood vessels that supply your brain.
Scientists used to believe that the brain’s blood supply and the brain itself were two completely separate entities, so it followed that researchers also believed that “neurodegenerative” diseases such as Alzheimer’s and “cerebrovascular” diseases such as a stroke caused by a rupture or occlusion of a blood vessel were completely unrelated processes.
The very concept of the NVU completely challenges that assumption and embraces the idea of a complex, symbiotic, mutually beneficial relationship between the brain cells and the cerebral blood vessels in both health as well as disease. The NVU serves as a weblike “interface” between your brain and the major blood vessels which supply it and consists of cerebral microvessels that receive constant neuronal input via signals from the neurons.
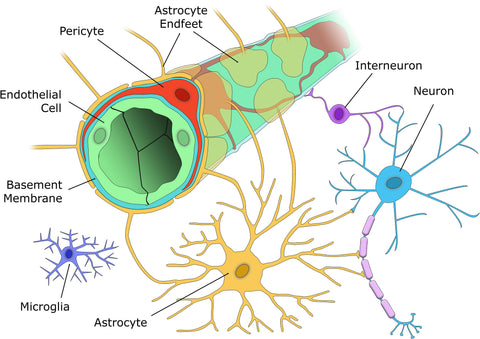
These specialized neuronal cells include such specialized structures as astrocytic endfeet, microscopic cellular membranes which cover the surface of the microvessels; as well as pericytes, cells embedded in the capillary walls; and perivascular microglia which constantly scavenge the central nervous system for infectious pathogens, damaged neurons and plaques. In addition, the network contributes to the stability of the blood-brain barrier, remodeling of the brain’s microcirculation and the control and removal of circulating inflammatory cells.

Research over the last decade demonstrates without a doubt that not only is the NVU an incredibly sophisticated, multidimensional, highly orchestrated system but that the development of neurodegenerative disease as well as cerebrovascular disease have their origin in pathology arising from the neurovascular unit. As you age, both the physical characteristics and function of the cells which make up the NVU become degraded, as do all the essential brain processes in which they are involved.
NAD And The NVU
So where does NAD come into all of this? We have discussed elsewhere - click here - the crucial role of NAD in the performance of the sirtuins (say “sir-TWO-ins”), a family of proteins known as the longevity genes, which regulate cellular aging, as well as mitochondrial function and inflammation among other processes.
There is also new evidence that indicates vascular (blood vessel) aging is also accompanied by depletion of NAD levels. Researchers have conclusively shown in mouse models that treatment with NAD bestows powerful anti-aging effects on the neurovascular system, including increased blood flow to the brain as well as improved cognitive performance. But even more astounding is evidence that treatment of vascular cells from aged rats (biological age of 24-month-old mice corresponds to that of approximately 60-year-old humans) which were treated with NMN for five day showed a restoration of youthful NAD levels and return of mitochondrial function.
A very recent study published in Geroscience (April, 2020) was designed to test the idea that the NAD depletion due to aging as seen in the NVU comes about as a result of the dysregulation of genes that are important for normal neurovascular function. The researchers also set out to see if they could find evidence that the aged mice whose neurovascular systems were restored with NMN treatment got better because of NMN’s positive effect on their SIRT-1 genes.
The researchers identified 590 genes that exhibited downgraded expression in the aged mice and 204 of those genes were restored to levels consistent with young mice after treatment with NMN. Further, the research also showed that the increased levels of NAD augmented SIRT1 activation in the NVU and is the first study to demonstrate that treatment with NMN in aged mice reverses to a great degree the age related inflammatory and cell dysfunction changes seen in the brain’s microcirculation.
Sirtuins, particularly SIRT1, do not function properly without adequate levels of NAD+. As NAD+ naturally declines with increasing age, it is vitally important to boost the availability of this powerful anti-aging coenzyme. As we have advised in the past, you could increase your level of NAD+ through the use of caloric restriction or a strict regimen of intermittent fasting, but for most people, these methods are simply not sustainable.
There has been much discussion within the scientific community on the difficulty of translating advances in research produced from animal (mouse) models to actual human clinical trials. This difficulty has been, in part, due to the extreme variability with which human subjects respond to various anti-aging interventions, whether those be drugs, exercise, supplement or dietary modifications such as calorie restriction.
A recent (2020) review of both privately and publicly funded human clinical studies conducted globally, found that supplementation with NAD+ precursors is a promising interventional strategy both to delay aging and to reduce age-associated maladies. Recent human clinical trials also showed that chronic supplementation with NR is well tolerated and stimulates NAD+ in middle aged and older adult subjects.
How To Increase Your NAD+ Levels
Taking a high quality NAD+ supplement is the most reliable and effective way to increase your NAD levels. There is evidence that for some types of cells, NAD+ and NADH can be directly imported into the cells. But in other cell types, there appears to be a dependency on importing NAD+ precursors (such as NMN) into the cell before it gets converted into the active molecule, so this may be a reason you may want to consider taking more than one type of NAD+ supplement.
You can find complete information on all of our NAD+ supplements here, including NAD+ as well as its precursor NMN. Taken every day, NAD+ supplementation will increase your levels of this powerful coenzyme and ensure you have the very best protection against the effects of the aging process, including aging’s detrimental effects on your neurovascular system. To your cognitive health!
References:
1. Ladecola C. The Neurovascular Unit Coming of Age: A Journey through Neurovascular Coupling in Health and Disease, (2017) Neuron, 96 (1) , pp. 17-42.
2. Kiss T & Nyúl-Tóth Á et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation promotes neurovascular rejuvenation in aged mice: transcriptional footprint of SIRT1 activation, mitochondrial protection, anti-inflammatory, and anti-apoptotic effects. Geroscience. 2020 Apr;42(2):527-546. doi: 10.1007/s11357-020-00165-5. Epub 2020 Feb 13. PMID: 32056076; PMCID: PMC7206476.
3. Tarantini S & Valcarcel-Ares MN et al. Nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) supplementation rescues cerebromicrovascular endothelial function and neurovascular coupling responses and improves cognitive function in aged mice. Redox Biol. 2019 Jun;24:101192. doi: 10.1016/j.redox.2019.101192. Epub 2019 Apr 10. PMID: 31015147; PMCID: PMC6477631.
4. Gonzalez-Freire, M., Diaz-Ruiz, A. et al. The road ahead for health and lifespan interventions, Ageing Research Reviews,Volume 59, 2020, doi.org/10.1016/j.arr.2020.101037.
5. Martens, C.R. & Denman et al. Chronic nicotinamide riboside supplementation is well-tolerated and elevates NAD(+) in healthy middle-aged and older adults. Nat. Commun., 9 (2018), p. 1286, 10.1038/s41467-018-03421-7.

